NCHS Releases New Reports This Week on Hearing Difficulty and Back/Limb pain among U.S. Adults
Posted on byNCHS Releases two new reports this week on hearing difficulty and back/limb pain.
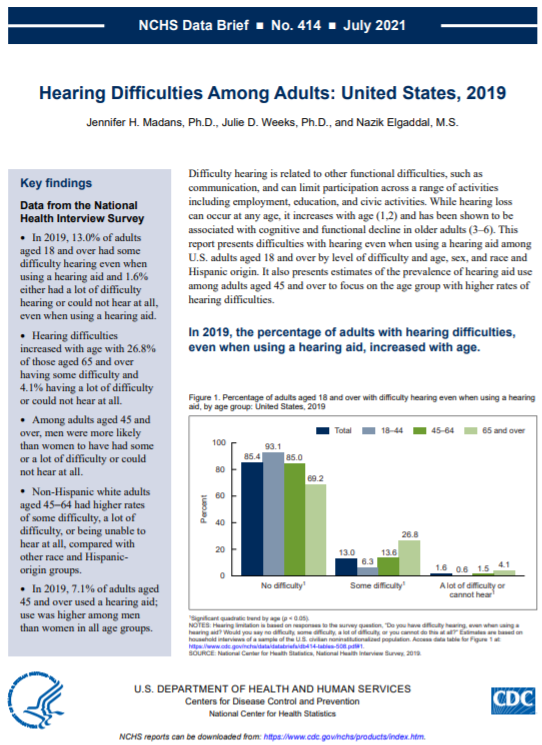 The first report presents difficulties with hearing even when using a hearing aid among U.S. adults aged 18 and over by level of difficulty and age, sex, and race and Hispanic origin. It also presents estimates of the prevalence of hearing aid use among adults aged 45 and over to focus on the age group with higher rates of hearing difficulties.
The first report presents difficulties with hearing even when using a hearing aid among U.S. adults aged 18 and over by level of difficulty and age, sex, and race and Hispanic origin. It also presents estimates of the prevalence of hearing aid use among adults aged 45 and over to focus on the age group with higher rates of hearing difficulties.
Key Findings:
- In 2019, 13.0% of adults aged 18 and over had some difficulty hearing even when using a hearing aid and 1.6% either had a lot of difficulty hearing or could not hear at all, even when using a hearing aid.
- Hearing difficulties increased with age with 26.8% of those aged 65 and over having some difficulty and 4.1% having a lot of difficulty or could not hear at all.
- Among adults aged 45 and over, men were more likely than women to have had some or a lot of difficulty or could
not hear at all. - Non-Hispanic white adults aged 45–64 had higher rates of some difficulty, a lot of difficulty, or being unable to
hear at all, compared with other race and Hispanic origin groups. - In 2019, 7.1% of adults aged 45 and over used a hearing aid; use was higher among men than women in all age groups.
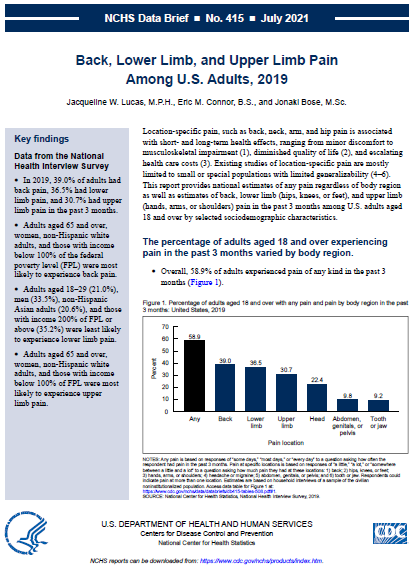 The second report provides national estimates of any pain regardless of body region as well as estimates of back, lower limb (hips, knees, or feet), and upper limb (hands, arms, or shoulders) pain in the past 3 months among U.S. adults aged 18 and over by selected sociodemographic characteristics.
The second report provides national estimates of any pain regardless of body region as well as estimates of back, lower limb (hips, knees, or feet), and upper limb (hands, arms, or shoulders) pain in the past 3 months among U.S. adults aged 18 and over by selected sociodemographic characteristics.
Key Findings:
- In 2019, 39.0% of adults had back pain, 36.5% had lower limb pain, and 30.7% had upper limb pain in the past 3 months.
- Adults aged 65 and over, women, non-Hispanic white adults, and those with income below 100% of the federal poverty level (FPL) were most likely to experience back pain.
- Adults aged 18–29 (21.0%), men (33.5%), non-Hispanic Asian adults (20.6%), and those with income 200% of FPL or
above (35.2%) were least likely to experience lower limb pain. - Adults aged 65 and over, women, non-Hispanic white adults, and those with income below 100% of FPL were most likely to experience
Posted on by

