Expenditures on Complementary Health Approaches: United States, 2012
Posted on byA new NCHS report presents estimates of expenditures on complementary health approach use among the U.S. population. Estimates are presented for adults and children separately and combined, as well as stratified by type of approach and family income.
Findings:
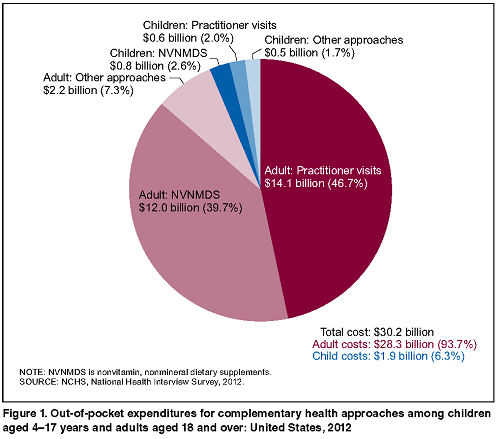
- An estimated 59 million persons aged 4 years and over had at least one expenditure for some type of complementary health approach, resulting in total out-of-pocket expenditures of $30.2 billion.
- More was spent on visits to complementary practitioners ($14.7 billion) than for purchases of natural product supplements ($12.8 billion) or self-care approaches ($2.7 billion).
- The mean per user out-of-pocket expenditure for visits to a complementary practitioner ($433) was significantly more than for purchases of natural product supplements ($368) or for self-care approaches ($257).
- Adults had higher mean annual out-of-pocket expenditures for visits to complementary practitioners than children ($442 and $291, respectively).
- Total out-of-pocket expenditures and mean per user out-of pocket expenditures for complementary health approaches increased significantly as family income increased.
- The mean per user out-of-pocket expenditure for complementary health approaches was $435 for persons with family incomes less than $25,000 and $590 for persons with family incomes of $100,000 or more.
Categories Uncategorized
Page last reviewed: June 23, 2016
Page last updated: June 23, 2016
Content source:
CDC, National Center for Health Statistics