More Adults taking using Cholesterol-Lowering Medicine
Posted on by Each year, more than 2 million Americans suffer from acute cardiovascular events that account for approximately one-fourth of the total cost of inpatient hospital care. Control of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL–C) has been shown to substantially reduce cardiovascular disease morbidity and mortality. It can be managed with lifestyle changes, medications, or a combination of these approaches. A diet low in saturated fat is recognized as one of the most effective lifestyle changes to decrease high LDL–C.
Each year, more than 2 million Americans suffer from acute cardiovascular events that account for approximately one-fourth of the total cost of inpatient hospital care. Control of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL–C) has been shown to substantially reduce cardiovascular disease morbidity and mortality. It can be managed with lifestyle changes, medications, or a combination of these approaches. A diet low in saturated fat is recognized as one of the most effective lifestyle changes to decrease high LDL–C.
NCHS has released a report that evaluates the trends in high LDL–C, use of cholesterol-lowering medication, and low dietary saturated-fat intake from 1976–1980 through 2007–2010 among adults aged 40–74.
Key findings from the report:
- The prevalence of high low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, or LDL–C, decreased from 59% to 27% from the late 1970s through 2007–2010.
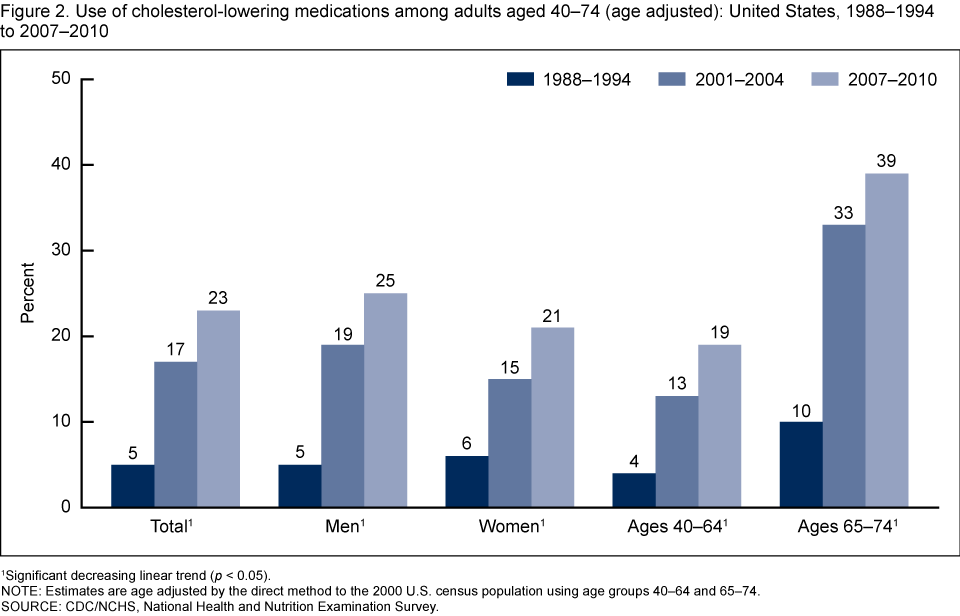
- The percentage of adults using cholesterol-lowering medication increased from 5% to 23% from the late 1980s through 2007–2010.
- The percentage of adults consuming a diet low in saturated fat increased from 25% to 41% from the late 1970s through 1988–1994.
- No significant changes in the percentage of adults consuming a diet low in saturated fat were observed from 1988–1994 through 2007–2010.
Posted on by