Search Results
10 results for population screening
Tier 1 Guidelines on Family-Based Screening for Hereditary Hemochromatosis

An important function in public health genomics is to identify evidence-based genomic applications that can save lives and prevent disease. In maintaining the PHGKB Tier Coded Guidelines database, we routinely look for Tier 1 applications of genomic testing strategies that have evidence-based guidance supporting implementation in specific clinical scenarios. We only consider recommendations that have
Posted on byGenomic Medicine Year in Review 2020: Population-wide Implementation Research Has Arrived

Advances in genomic medicine continue at a steady pace. In a December 2019 paper, The Genomic Medicine Working Group of the National Advisory Council for Human Genome Research of the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) identified 10 papers with the most significant advances in the field. In our 2019 end of the year blog. we featured 5
Posted on byImplementation Science to Improve Case Finding, Cascade Screening, and Treatment for Familial Hypercholesterolemia: A Prototype for Precision Public Health Research
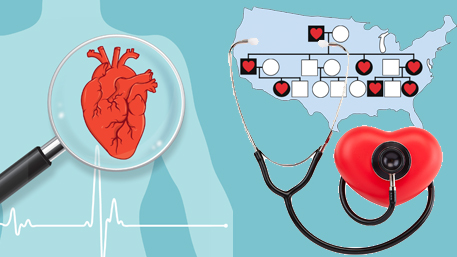
Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a common genetic disorder, affecting more than 1 million people in the United States. FH causes lifelong high levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and if untreated, leads to a high risk of premature coronary heart disease. Most patients with FH are undiagnosed or inadequately treated with regular or high-intensity statins, leaving
Posted on byShould polygenic risk scores be used in risk-stratified colorectal cancer screening?
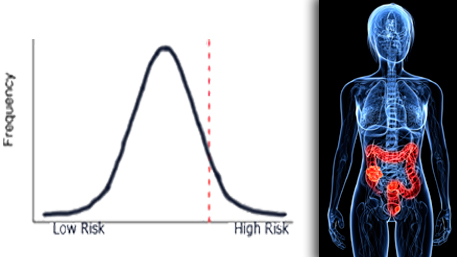
Polygenic risk scores (PRS) summarize information about a person’s disease risk based on numerous DNA variants in their genome. Each variant confers very little increase in disease risk. But composite (or polygenic) risk scores made up of a number of such variants have been shown to stratify people to normal distributions of disease risks for
Posted on byPublic Health Perspectives on Ensuring Life Long Benefits of Newborn Screening
This blog post is a summary of a Perspective recently published in Pediatrics that was authored by Alex Kemper of Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Jeffrey Brosco of the Miller School of Medicine, University of Miami, and Coleen Boyle and Scott Grosse of CDC’s National Center on Birth Defects and Developmental Disabilities. Newborn screening is a highly
Posted on byContributions of Public Health in Reducing the Population Burden of Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Challenges and Opportunities
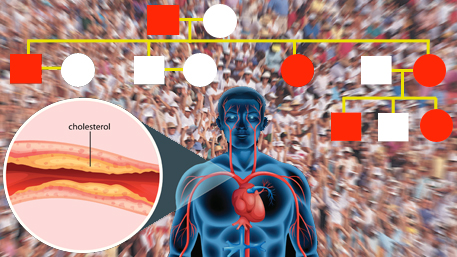
In October 2018, we attended the fifth annual Global Familial Hypercholesterolemia (FH) Summit. This gathering of more than 300 people from over 30 countries included patients, researchers, government organizations, practitioners, health systems, implementation science experts, and industry. The event focused on methods for accelerating uptake of evidence into clinical practice and health policy. The event
Posted on by 1 CommentA Road Map for Evaluation and Appropriate Implementation of Genome Sequencing to Improve Population Health

This blog is a summary of our recently published paper in PLOS Medicine, and is an update of my 2011 blog on “binning” the human genome. A common vision for genomic medicine is that genome sequencing will be routinely used in health systems to provide health care and preventive services tailored to each individual. For
Posted on byUsing Genetic Risk Scores in Cancer Screening: Are We There Yet?

Precision screening seeks to measure benefits and risks of screening more accurately by accounting for individual-level differences, such as those in genetics, environment, and lifestyle factors. Accounting for individual differences may allow risk stratification to identify persons whose cancer risk is high enough that the benefits of screening would outweigh potential harms or whose cancer
Posted on byUniversal Screening for Lynch Syndrome: Can Tumor Sequencing Have a Larger Public Health Impact on Treatment and Prevention of Colorectal Cancer?

Lynch syndrome (LS) is the most common hereditary syndrome associated with increased risk of colorectal cancer (CRC), accounting for about 3% of CRC patients. LS is a dominantly inherited condition with mutations in several mismatch repair (MMR) genes. Persons with LS are also at increased risk for endometrial and other cancers. Lynch syndrome affects 1
Posted on byPrecision Medicine in Action: How well does cascade screening for hereditary conditions work in the real world?
An important component of precision medicine is the identification, through genetic testing, of people who are at elevated risk of disease because of pathogenic germline mutations. Cascade screening involves contacting relatives of patients with certain hereditary conditions to help inform, manage, and identify those who may be at increased risk. A systematic scoping review on
Posted on by

