Genomics and Precision Health Blog – Archive Posts
Tracking the Translation of Genomic Discoveries to Population Health Benefits: Connecting the Dots from Investment to Population Health Information

In March 2018, the CDC Office of Public Health Genomics launched the Grant Database (GDB), an extension of the Public Health Genomics Knowledge Base (PHGKB). GDB “connects the dots” between funding investment and publications on translation, implementation, and evaluation of population health impact of genomics and precision medicine. We launched PHGKB in 2016, as an Read More >
Posted on byGenomics and Population Health Action: The Collaboration Continues!

In March 2018, I attended the third annual meeting of leaders of the Genomics and Population Health Action Collaborative (GPHAC). GPHAC was formed late in 2015 under the auspices of the National Academy of Medicine’s Roundtable on Genomics and Precision Health to foster collaboration of more than 50 diverse stakeholders, including state public health programs, Read More >
Posted on byFamilial Hypercholesterolemia is Common and Undertreated in the United States
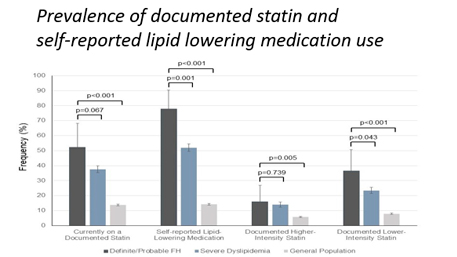
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder that significantly increases the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and premature deaths from heart attacks and stroke. The national prevalence of FH and rates of screening, awareness, and treatment with statins among individuals with FH and other causes of high lipid levels (dyslipidemias) remain largely unknown. Read More >
Posted on byLeap of Faith or Smart Investment? Early Integration of Whole Genome Sequencing in Healthcare Systems

Discovery science in genomic medicine has generally enjoyed longstanding large collaborations for data sharing and joint analyses. Synergies among collaborators has accelerated major advances in our understanding of the genetic basis of health and diseases. More recently, some of the same scientists have come together to aggregate data for more applied clinical research with NIH Read More >
Posted on byHLBS-PopOmics: NHLBI and CDC partner to launch a public health genomics knowledge base for heart, lung, blood, and sleep disorders

Timely and targeted dissemination of published research findings is an important step in accelerating the pace of turning discovery into health. To achieve this goal in human population genomics, the NHLBI has partnered with the CDC Office of Public Health Genomics (OPHG) to launch a heart, lung, blood, and sleep disorders knowledge base in population Read More >
Posted on bySaving a Million Hearts: One Heart at a Time!

Cardiovascular disease (CVD), principally ischemic heart disease and stroke, remains the leading cause of U.S. deaths for men and women and all races and ethnicities in spite of major progress in its prevention and treatment. CVD is also the greatest contributor to racial disparities in life expectancy. In 2012, 120 public and private partners and Read More >
Posted on byDear John, There’s no point in waiting any longer. Let’s call it quits…

In 1999, Dr. Francis Collins, director of the Human Genome Project, provided a bold vision for what the practice of genomic medicine might soon look like. Collins described the case of a hypothetical man named “John,” a 23 year-old smoker living a decade into the future in 2010. “His substantial risk of contracting lung cancer Read More >
Posted on by 4 CommentsWork in Progress: Classifying Evidence-based Genomic Applications for Practice and Prevention
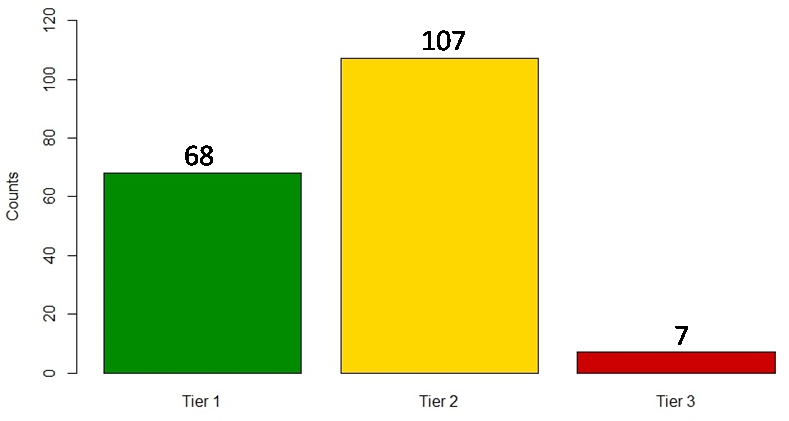
In our 2015 paper,“Prioritizing genomic applications for action by level of evidence: A horizon-scanning method,” we proposed a systematic scanning method that assigns genomic applications to “tiers” defined by availability of synthesized evidence. Because of the amassed evidence on the validity and utility of genomic tests and related technologies, we suggested that researchers, policy makers, Read More >
Posted on byWhat do women (and men) want? Parents weigh in on genetic testing for rare diseases in children

Genetic testing in children has traditionally focused on conditions with clinical actionability or utility. However, parents may want to know whether their child is at high risk of a rare disease even if a treatment doesn’t exist. A newly published article reports on a study conducted by researchers at RTI International and the University of Read More >
Posted on byGenomics and Obesity: We Need Both Population and Individualized Approaches in the Prevention and Management of Obesity

Obesity is a serious, global public health problem that has increased markedly in the last few decades. As of 2016, 795 million people were estimated to have been affected. Obesity is associated with leading causes of death worldwide—such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer—making the search for effective weight management strategies a global priority. Obesity Read More >
Posted on by 2 Comments

