Welder’s Anthrax
Posted on by
A new journal article from researchers at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) and the Bacterial Special Pathogens Branch describes cases of welder’s anthrax, a newly identified, deadly occupational disease.
Welder’s anthrax is defined as pneumonia in a metalworker caused by bacteria within the B. cereus group that produces anthrax toxin. Seven patients diagnosed with what is now termed welder’s anthrax were reported to the CDC from 1994–2020. The job title of six patients was welder, and the job title of the seventh was metalworker. All were confirmed to be infected with B. cereus group bacteria containing anthrax toxin genes. Six of the workers were men. The median age was 39 years. Four of the patients worked in Texas and three in Louisiana.
Information on the type of welding, job activities, and type of workplace, including indoor or outdoor activities, was limited for most of the patients except for the two patients diagnosed in 2020. One patient worked on the roof of an oil tank outdoors. He welded on new A36 mild carbon steel using a shielded metal arc welding (or stick) process. The other patient worked in a wood fabrication shop. He welded on low-carbon mild steel using Metal Inert Gas (MIG) with solid or flux core wire and 75% argon/25% carbon dioxide shield gas. Both patients performed additional tasks such as scrubbing debris with a wire metal brush and grinding. Both reportedly wore respiratory protection during welding activities.
Of the six patients with available data on signs and symptoms, over half presented with each of the following: fever or chills, cough, shortness of breath (dyspnea), and coughing up blood (hemoptysis). All had abnormal chest radiographs and were diagnosed with pneumonia. All were hospitalized and were admitted to the intensive care unit if they survived past the emergency department. Five of the seven patients died. All patients received broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment. One of the surviving patients received raxibacumab, a monoclonal anthrax antitoxin.
Welders at Increased Risk
Several studies have shown an increased risk of pneumonia and death among welders and other workers exposed to metal fumes and mineral dusts [1-6]. Research suggests it is possible that exposure to metal fumes might increase susceptibility to lung infection, even with common, relatively harmless infectious agents [7]. Furthermore, iron oxide deposited in the lungs after inhaling welding fume has been found in the lungs for years, even after removal from exposure [8].
How metal fumes cause disease is mostly unknown. Theories include that metal fumes (or iron) act as a growth nutrient for bacteria, enhance the binding of bacteria to lung tissues, or impair immune responses in the lung through oxidative stress [1,5,6,9]. Like all pathogens, B. anthracis and B. cereus anthrax toxins need iron to survive and thrive.
While iron overload might partially explain the increased susceptibility of welders for B. cereus infections, exposure is still important. Several researchers have noted that soil iron is much higher around welding sites than elsewhere [10,11]. Future research measuring soil iron levels may provide useful information.
Prevention
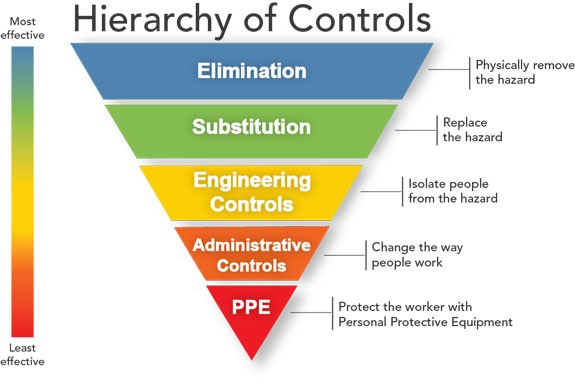 The hierarchy of controls can be used to prevent workplace exposure to welding fumes and gases, and soils that may be contaminated with B. cereus group bacteria producing anthrax toxins.
The hierarchy of controls can be used to prevent workplace exposure to welding fumes and gases, and soils that may be contaminated with B. cereus group bacteria producing anthrax toxins.
- Employers should conduct a hazard assessment on all welders, other metalworkers, and supervisors at worksites.
- Elimination and substitution controls to help reduce exposure to fume and gases from welding and soils that may be contaminated with cereus group include:
- Using a less toxic welding type or consumable.
- Ensuring that welding surfaces are free of any coatings, dirt, and dust that may lead to potentially toxic exposures.
- Engineering controls can include the use of general and local exhaust ventilation. Do not assume that welding outdoors or in open areas provides adequate general ventilation, even when the welder uses proper positioning and natural drafts. Local exhaust systems should be positioned to draw fume and gases away from the welder and other workers in the area.
- Administrative controls include maintaining a clean and dirt-free worksite.
- Workplaces should be routinely cleaned with a vacuum equipped with a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter or wet cleaning methods.
- Compressed air and dry sweeping or brushing should not be used.
- Dust control programs in outdoor workplaces and near workplaces open to the outdoors can minimize dirt and dust exposure, and activities in the immediate vicinity should be limited to help minimize disturbing dry dust.
- In surrounding areas, adding water, hydroscopic compounds, or surfactants to roadways and surfaces that are heavily traveled can help control dirt and dust exposures. However, these substances should not be applied in the immediate area where welding occurs as this may cause an electrocution hazard.
- Welders and other metalworkers must understand their potential occupational health risks and how to protect themselves. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration’s (OSHA’s) Hazard Communication Standard requires employers to inform and train workers on potential work hazards and associated safe practices, procedures, and protective measures.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE) may include coveralls and work boots in the workplace to prevent their skin and clothing from being contaminated and taking contaminants home. NIOSH-approved respirators, as part of a written respiratory protection program, may be needed when other controls do not reduce exposures to safe levels.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Physicians should consider welder’s anthrax in welders who present with pneumonia, particularly those working in U.S. Gulf Coast states. Welders and other metalworkers who present with welder’s anthrax should be treated the same as a patient with inhalation anthrax.
If infection with anthrax toxin-expressing B. cereus group is suspected, it is important to notify the state health department; a consultation with CDC is recommended. Anthrax antitoxins should be considered as adjunctive therapy if the patient’s clinical condition suggests systemic illness. However, the role of anthrax vaccine pre- or post-exposure for welders is not currently recognized or understood.
Next Steps
It is possible that cases of welder’s anthrax were missed due to limited detection and understanding of anthrax toxins, underdiagnosis, and under-reporting of the patient’s occupation. To improve data collection in surveillance systems, the NIOSH Surveillance Program recommends that occupational questions should be standardized, and information on both industry and occupation should be collected and analyzed. Other helpful information for the investigation of welder’s anthrax includes the employer’s name, work location, job duties, and questions about specific types of welding, metals, and other exposures and protective measures taken.
Communication and cooperation between clinicians, employers, and public health practitioners is important to identify cases of welder’s anthrax and occupational and personal risk factors. More research is needed to better understand the mechanisms of infection and disease among welders. Additional research is needed to better understand how exposure to metal fumes and other welding hazards may increase susceptibility to and severity of lung infection in welders. The effectiveness of interventions to minimize workers’ exposure to metal fumes, including engineering controls and respiratory protection, should also be explored.
Welder’s anthrax is a new and rare disease. We would like to raise awareness of this infection among welders and clinicians. If you have ideas for how to do so, please contact us through the comment section below.
Marie A. de Perio, Chad H. Dowell, Nancy C. Burton, Karl Feldmann, and James M. Antonini are with the CDC’s National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health.
Katherine A. Hendricks, William A. Bower, Caroline A. Schrodt, Johanna S. Salzer, Chung K. Marston, and Alex R. Hoffmaster are with the CDC’s National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases.
Patrick Dawson is with the CDC’s Office of Science.
References
- Torén, K.; Blanc, P.D.; Naidoo, R.N.; Murgia, N.; Qvarfordt, I.; Aspevall, O.; Dahlman-Hoglund, A.; Schioler, L. Occupational Exposure to Dust and to Fumes, Work as a Welder and Invasive Pneumococcal Disease Risk. Environ. Med. 2019, 77, 57–63.
- Koh, D.H.; Moon, K.T.; Kim, J.Y.; Choe, S.W. The Risk of Hospitalisation for Infectious Pneumonia in Mineral Dust Exposed Industries. Environ. Med. 2011, 68, 116–119.
- Torén, K.; Qvarfordt, I.; Bergdahl, I.A.; Järvholm, B. Increased Mortality from Infectious Pneumonia after Occupational Exposure to Inorganic Dust, Metal Fumes and Chemicals. Thorax 2011, 66, 992–996.
- Wong, A.; Marrie, T.J.; Garg, S.; Kellner, J.D.; Tyrrell, G.J.; SPAT Group. Welders Are at Increased Risk for Invasive Pneumococcal Disease. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 14, e796–e799.
- Palmer, K.T.; Cullinan, P.; Rice, S.; Brown, T.; Coggon, D. Mortality from Infectious Pneumonia in Metal Workers: A Comparison with Deaths from Asthma in Occupations Exposed to Respiratory Sensitisers. Thorax 2009, 64, 983–986.
- Marongiu, A.; Hasan, O.; Ali, A.; Bakhsh, S.; George, B.; Irfan, N.; Minelli, C.; Canova, C.; Schofield, S.; De Matteis, S.; et al.. Are Welders More at Risk of Respiratory Infections? Findings from a Cross-sectional Survey and Analysis of Medical Records in Shipyard Workers: The WELSHIP Project. Thorax 2016, 71, 601–606.
- Lockey, J.E.; Schenker, M.B.; Howden, D.G.; Desmeules, M.J.; Saracci, R.; Sprince, N.L.; Harber, P.I. Current Issues in Occupational Lung Disease. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1988, 138, 1047–1050.
- Kalliomaki, P.-L.; Kalliomaki, K.; Rahkonen, E.; Aittoniemi, K. Lung Retention of Welding Fumes and Ventilatory Lung Functions. A Follow-Up Study among Shipyard Welders. Occup. Hyg. 1983, 27, 449–452.
- Coggon, D.; Inskip, H.; Winter, P.; Pannett, B. Lobar Pneumonia: An Occupational disease in Welders. Lancet 1994, 344, 41–43.
- Dheeba, B.; Sampathkumar, P. Evaluation of Heavy Metal Contamination in Surface Soil around Industrial Area, Tamil Nadu, India. J. Chem. Tech. Res. 2012, 4, 1229–1240.
- Adekeye, E.A.; Ojo, M.A.; Ajayi, O.O. Contributions of Metal Welding Workshops to Environmental Pollution in Akure Metropolis, Ondo State, Nigeria. Environ. Iss. Agric. Dev. Ctry. 2011, 3, 1–7.
Posted on by

