Category:
Genomics and Obesity: We Need Both Population and Individualized Approaches in the Prevention and Management of Obesity

Obesity is a serious, global public health problem that has increased markedly in the last few decades. As of 2016, 795 million people were estimated to have been affected. Obesity is associated with leading causes of death worldwide—such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer—making the search for effective weight management strategies a global priority. Obesity Read More >
Posted on by 2 CommentsThe Impact of Family History on the Public Health Burden of Diagnosed Diabetes, Undiagnosed Diabetes and Prediabetes in the United States: Using Family History for Diabetes Control and Prevention

This blog post is a summary of our recently published paper in Genetics in Medicine. Type 2 diabetes is a major public health problem in the United States and globally. Among adults 20 years and older, 9.2% have diagnosed diabetes (DD), 3.1% have undiagnosed diabetes (UD), and 36% have prediabetes (PD), a major precursor for Read More >
Posted on byProgress in Public Health Genomics Depends on Measuring Population Level Outcomes

Public health genomics is a relatively young field concerned with the effective and responsible translation of genomic science into population health benefits. In the past few years, the field has witnessed the emergence of several state public health genomics programs beyond the traditional domain of newborn screening. The field has focused on preventing disease and Read More >
Posted on byTrends in CDC Publications in Public Health Genomics, 2012-2016
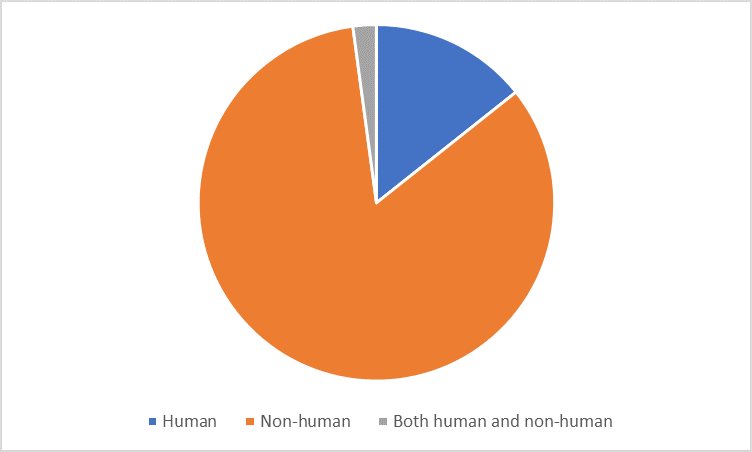
Public health genomics advances the translation of genome-based discoveries into disease prevention and population health. Scientists at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) are using information about human, vector, and pathogen genomes to tackle diverse public health problems, from newborn metabolic disorders to infectious disease outbreaks. For an overview of CDC publications in Read More >
Posted on by

